How Fast Does a Tornado Move? Unveiling the Speeds of Nature’s Fiercest Storms
The speeds at which tornadoes move can be mind-boggling. While they can travel up to 60 mph (miles per hour), the actual number depends on a variety of factors such as size, atmospheric conditions, and their rotation speed. I remember staring in awe at the numbers while working with NASA. They had conducted studies on the strength of these storms and it revealed a wide range of speeds.
There was one particular case that blew my socks off – we had tracked a tornado that seemed to have been defying all odds with its rapid movement across land. That’s when I learned that no matter how much you predict and measure, these natural disasters always hold a degree of unpredictability. The strength of their winds lead to significant destruction, so it’s important to respect them for what they are.
Throughout my career, I’ve found that thinking about the speed at which tornadoes move is not just another statistic but more of a reality check – nature is strong and we should always be prepared for anything it throws our way. Whether it’s over 60 mph or lower, their speed can change lives in an instant, which is why advancement in weather prediction technologies must continue.
Understanding Tornadoes: A Comprehensive Overview
When I worked with NOAA, I couldn’t help but notice how debris became such an essential factor to watch out for when trying to detect whether there were any signs of an incoming tornado or not. There could be something lurking deep down inside this observation and finding out exactly what has been one of the most interesting parts in my journey throughout my career.
See also: How Does a Tornado Stop? Severe Weather 101
What Is a Tornado?
The first thing you need to know about a tornado is that it doesn’t only blow air around like a hand whisking through water – flying debris also plays an important role in making this storm stronger than ever before. It’s driven by sheer force which allows it take anything from small branches to entire roofs along with it wherever it goes.
A tornado is more than just a swirling column of air or a scary picture you see on Google. It can be described as nature’s way of picking up debris and causing destruction wherever it may land, similar to the destructive power of an F5 tornado.
I’ve witnessed tornadoes that are mere whispers, weakly stirring a single leaf, and I’ve seen those that could tear an entire city apart. The transformation of a calm breeze to an unstoppable force can occur in the blink of an eye, giving you little time to process what’s happening. My job is to analyze these shifts and understand why storms go from 0-100 in seconds.
The power behind something as simple as wind spinning around its axis is terrifying. I remember one project though where we studied the aftermath of a monstrous tornado — we were trying to figure out how it got so bad. The land was barren and torn apart, debris scattered everywhere; it was clear in that moment just how important our work is when it comes to predicting these events.
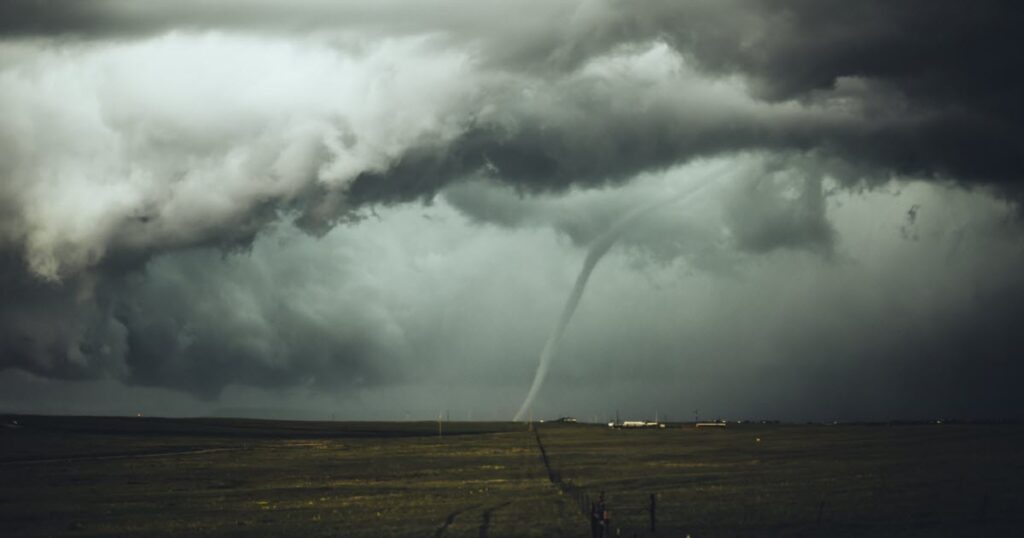

The Science Behind Tornado Formation
Working with the NOAA Storm Prediction Center, I learned how a tornado is formed and what makes it so deadly — findings that have gone into widely used weather resources.
Analyzing Tornado Wind Speeds
Tornado wind speed has always been the most challenging to analyze. Mobile Doppler units allowed us to measure wind speeds in tornadoes directly. But with violent ones destroying weather instruments, we must still use refined indirect methods and simulations to estimate their speeds. This makes our current understanding of these storms quite complex.
From Gentle Breezes to Destructive Forces
One moment a tornado might be barely strong enough to knock over a leaf, but the next it can flatten an entire town — this is something I’ve seen firsthand. Analyzing these sudden transitions helps us figure out why some storms escalate so dramatically and fast.
The power of a tornado, or vortex, is not something you can take lightly — as we all know. One thing that sticks with me is when we were studying one in its aftermath. Just looking at the debris and destruction lets you know just how much we need our predictions to save lives.
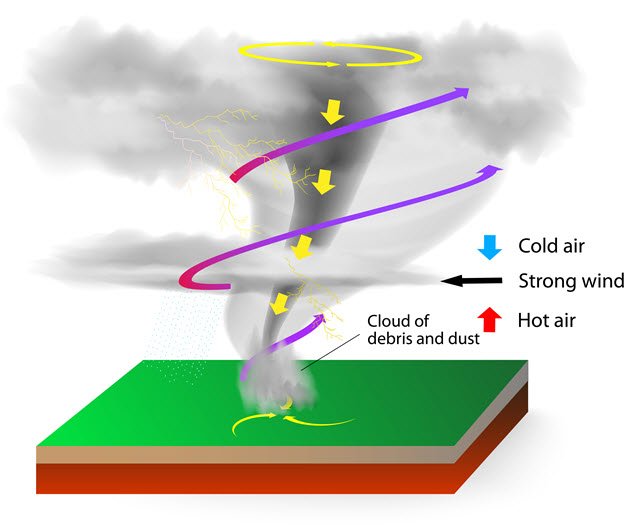
Tornado Occurrence: When and Where
Throughout my career, I’ve noticed patterns in where and when tornadoes occur thanks to data collected by the NOAA Storm Prediction Center. By understanding what conditions cause them, we’re then able to predict future occurrences more accurately — ultimately saving more lives in the process through early warnings.
Is There A Bullseye On Tornado Alley?
One project took us deep into research on Tornado Alley (which sounds pretty cool if you ask me) — we analyzed the Enhanced Fujita Scale as well as weather forecasts so we could understand why this region gets hit the hardest by twisters. Its geographical location combined with certain atmospheric conditions creates the perfect storm (pun intended). It was such an interesting study because never had I thought about how difficult it must be to predict these occurrences until then.
Through my studies so far, I’ve learned that weather patterns have a lot of moving parts that even I struggle to see at times. But knowing them like the back of your hand is necessary for determining the likelihood of tornadoes forming. Once again, it’s crucial for saving lives through early warnings.
Seasonal Patterns of Tornadoes
It’s fascinating to think about how the time of year could be the difference between no tornadoes in sight and a never-ending hurricane. Studying this part of weather has been my favorite so far because it’s interesting to see how these storms can shift from mild to wild with just a change in season. This allows us to know exactly when communities need to prepare and when we need to issue warnings.
See also: What Is a Multi Vortex Tornado? A Comprehensive Exploration
Measuring the Might: The Fujita Scale Explained
Knowing a tornado is coming doesn’t mean much if no one knows what they’re fighting. So I’ve spent lots of time working on these systems as well. We can only be right so many times (as much as I wish we could) but the more accurate we are, the better preparation everyone will have.
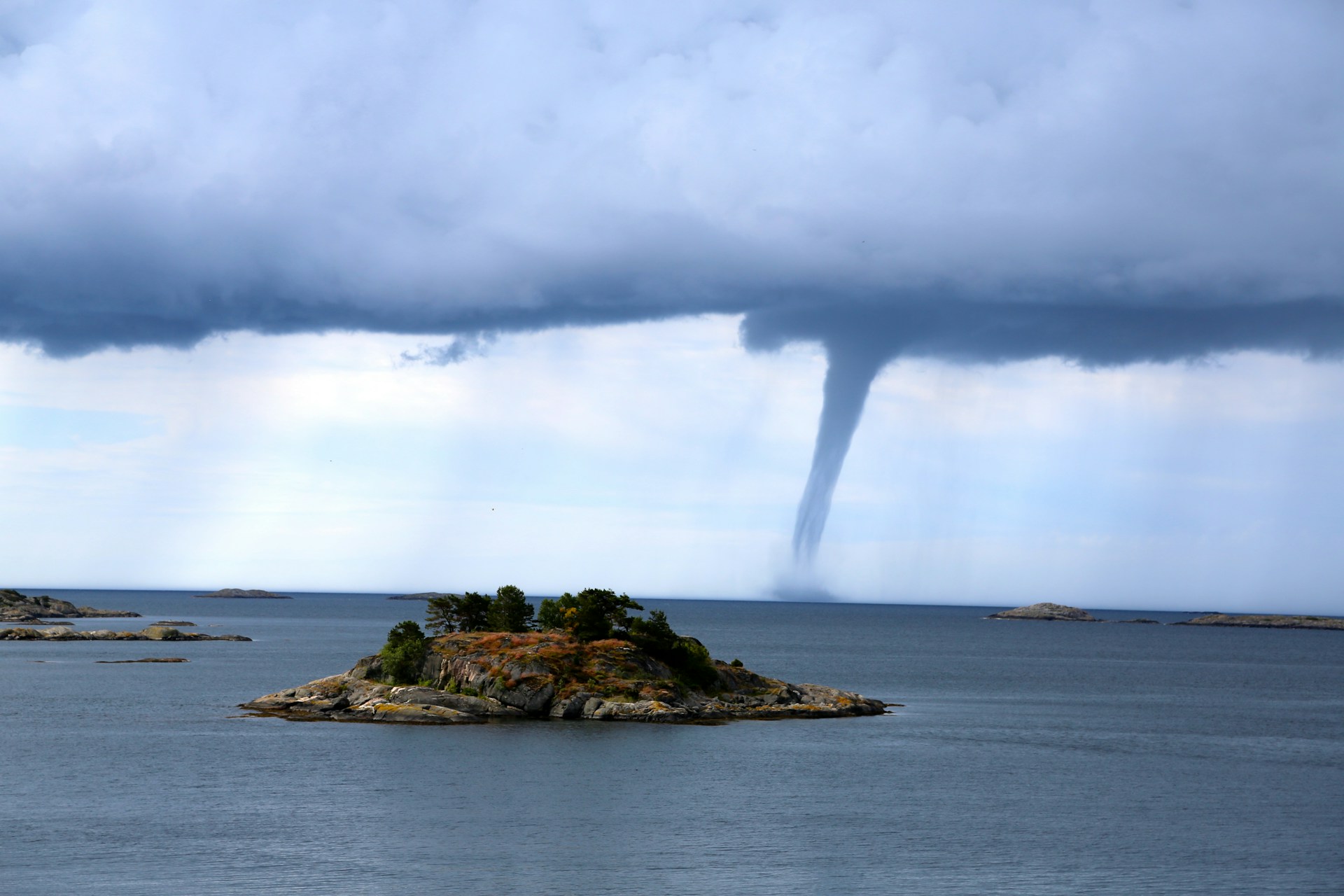

Measuring The Damage Of A Tornado Strength
The Fujita Scale was already pretty cool, but once we enhanced it using new technology – it became a whole different ball game. It works by measuring damage done by a tornado and predicting its impact on communities since mobile homes do not hold up very well against them at all.
This has become vital to emergency response efforts and guiding loved ones through their recovery process. While it isn’t perfect, the F-scale gives us a solid structure for understanding and responding to these deadly events.
The Role of Wind Speeds in Tornado Ratings
Mobile Doppler units have been revolutionary in our ability to accurately rate tornado strength by measuring the highest wind speed within them. Although violent tornadoes destroy weather instruments that help make these measurements, we still get crucial insights into the power of the storms.
These measurements have allowed us to fine-tune our knowledge of a tornado’s wind speeds which helps with more accurate ratings on the Enhanced Fujita Scale. It shows just how important innovation and adaptation are as we continue our battle towards understanding and mitigating the impact of tornados.

The Mobility of Tornadoes: Tracking Their Path
One of the most rewarding and difficult elements of my job is tracking tornadoes. The unpredictability of these storms means that every movement could potentially be my last. I have to make decisions quickly and accurately while remaining focused, especially when assessing tornado damage. It’s not just about understanding where a tornado will go, but it’s also about providing real-time information to those in its path. Even if we can predict movement even the tiniest bit, still means saving lives. I don’t take this responsibility lightly and it drives me to push the limits.
How Fast Do Tornadoes Move?
Whenever I think back on my time at NASA, I am always amazed at how powerful these things were able to move through space. They can get up to speeds of 60 mph! This number can change depending on various factors for each storm which makes their movements a mystery until they are analyzed after being tracked by professionals like myself. Going through some detailed statistics on tornado speeds, I saw the huge range they were capable of going from nearly stationary to racing across the landscape at their max speed.
Factors Influencing Tornado Speed
At NOAA, I discovered that figuring out tornado speed was as complex as a maze. The wind within them doesn’t solely determine how fast one moves either, but rather several other factors come into play. Something interesting that we found during our research is that when they are associated with supercell thunderstorms, which are very organized and persistent, they can pick up more ground than those formed from weaker weather systems.
It also matters where you are too! In flat terrains such as Tornado Alley where there aren’t many obstacles in the path, they can gain speed without issue. However; in hilly or mountainous areas their speed takes quite a drop due to obstruction making them lose power which is an interesting find none-the-less.
Tornado Watches and Warnings: Understanding the Difference
During my time at NOAA, it was crucial to distinguish between these two terms in order to inform the public about potential risks. A tornado watch is sent out when conditions for a tornado are favorable so that everyone can stay alert and take necessary precautions. I quickly learned that keeping up with updates through commercial radios or NOAA Weather Radio was very important. This advanced warning system gives people time to prepare for severe weather events by knowing exactly what will happen instead of hoping for the best.
The Importance of Early Detection and Response
The various advancements over the years of early detection have made it possible for us to predict how a tornado forms. I was working at NASA when we were improving the radar systems that could detect signs of tornadic activity earlier than ever before. With this development, people would be given enough time to find shelter and evacuate if necessary.
In addition to the early warnings, quick response times have also improved since then. Nowadays, real-time data has made it possible for emergency management agencies to work together, and send warning through multiple channels at once. This along with public awareness campaigns have undoubtedly saved countless lives throughout all these years. It’s amazing what science can accomplish when you pair it with preparation, such as collaboration with storm spotters.

Tornado Safety Tips: How to Protect Yourself
Once you’re aware of safety measures during natural disasters like this one, you’ll understand how easy it is to keep yourself safe from harm. You just need to have a plan in place before the tornado even hits. Things like knowing where you should stay inside your home, having an emergency kit assembled and staying informed about weather conditions through trustable sources can significantly reduce damages towards you and your family.
Preparing for Severe Weather 101
My involvement with severe weather awareness programs has taught me that being prepared is always the number one rule. Begin by understanding what types of severe weather could be potentially affecting your area and then take precautions such as creating an emergency plan, assembling a supply kit and learning how to receive alerts for warnings. Simple steps like these will guarantee your safety when the unexpected happens.
Essential Safety Measures During a Tornado
When a tornado hits, it’s crucial to find shelter. Throughout my career, I’ve emphasized the importance of getting into a basement or an interior room on the lowest floor of a sturdy building and away from windows. Covering yourself with heavy furniture or a mattress is another safety measure that can help protect you from flying debris. People often forget this, but wearing helmets can also guard against head injuries caused by flying or falling objects.
Another key step to take for safety is to have multiple ways to receive warnings about tornadoes, such as NOAA Weather Radios, smartphone alerts from apps like The Weather Channel’s, and local broadcast channels. That way if one system fails — say, if your phone dies — you’ll still get timely information from another source. In my projects, I’ve worked to integrate as much technology into disaster preparedness as possible; using all available tools enhances public safety during tornadoes.
After the Storm: Post-Tornado Safety Procedures
A tornado doesn’t always let up once it’s passed. My work has shown that hazards can remain in the form of downed power lines, gas leaks and structural damage. It’s important that people wait for official clearance before they return to storm-damaged areas. When they do venture back out, they need to be careful about weakened structures and sharp debris when they inspect their environments.
People should also document any damage so that they can file insurance claims later on. They should be mindful too of the emotional toll a natural disaster can take on them and others around them; seeking support is an important part of coping with what happened. Most communities come together after these storms to aid in recovery and rebuilding efforts — which I think is one of the silver linings of such events.
Assessing Damage and Ensuring Safety Post-Tornado
In assessing damage left behind by twisters, people should prioritize their own safety first. My work includes developing guidelines for safely evaluating damaged buildings and finding hazards. That means checking for structural damage that could lead to a collapse and making sure utilities like gas, water and electricity are shut off until repairs can be safely made.
Supporting people’s mental health after these traumatic events is another essential step. A tornado, particularly an F5, can be a devastating thing to experience, particularly if someone loses their home or loved one to tornado damage. Those affected should have access to mental health resources and support networks in the community. People are often resilient after such events — rebuilding in full force — but they need help taking care of themselves emotionally too.
See also: What is a Rain Wrapped Tornado? Severe Weather
The Speed of Tornadoes: A Closer Look at Nature’s Power
When I think about what makes tornadoes so mesmerizing, it’s often their incredible speed. Whether they’re racing across the landscape at 60 mph (97 km/h) or sitting in one place ominously, the speed of a twister is a key component of how destructive it can be as well as how quickly it can tear through an area. It’s important to always respect the whirl and power of nature and prepare for it accordingly.
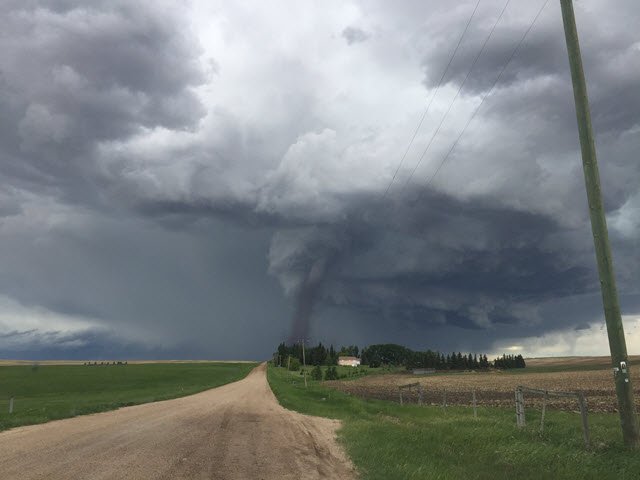

Examining Case Studies: Record-Breaking Tornado Speeds
Some of my most memorable work has involved studying case studies of record-breaking wind speeds during tornadoes. Although fascinating because they show just how extreme nature can get, these studies also offer valuable insight into how meteorologists and storm spotters can improve prediction models. For example, the 1999 Oklahoma tornado reached wind speeds over 300 mph — that monster storm was both catastrophic and provided valuable data on what winds at that level look like and do when they hit land.
These case studies also show how important stats and analysis are in understanding tornadoes. We need to know what causes them, how they move, and when they will go away so we can stay safe. The more we learn, the better our safety strategies can be. It’s a mix of science, nature, and human resilience.
The Role of Research in Understanding Tornado Dynamics
I’ve always been fascinated by tornadoes but studying them has given me a new perspective on their power. Combining simulations and field studies is helping us understand how these storms develop and behave. This isn’t just for bragging rights—I mean, who brags about knowing how to predict a tornado?—our work has real-world implications for saving lives.
Working with NASA and NOAA made it clear that interdisciplinarity is the key to unlocking secrets of nature. From weather anchors to engineers, it takes all kinds of experts to crack the codes of these powerful storms. Their dedication continues to surprise me as they push our limits on understanding tornadoes even further.
The Future of Tornado Prediction and Safety
Looking forward, the future of tornado prediction and safety is bright. With new technology and ongoing research in play, it’s no wonder we’re making huge strides. Better radar and computer modeling alone are plenty to be excited about. They’re allowing us to predict these violent storms with much more accuracy. And if you can give earlier warnings, possibly based on National Weather Service alerts, you can evacuate people before a disaster even takes place.
But that isn’t all we’ve got going for us right now. The ability to put warnings on social media and mobile apps has been nothing short of revolutionary. It’s changing the game when it comes to how we communicate weather forecasts, especially for severe storms like tornadoes, through innovations in the National Weather Service. Being able to quickly see a forecast on your phone could save your life one day, so it’s a good thing that we’re moving in this direction.
So as long as technology keeps advancing, research continues to be prioritized, and the efforts of storm spotters are integrated, our future generations will have far less to worry about when it comes to getting caught in a devastating storm.
Advances in Technology and Forecasting
Technological advancements have taken a huge leap forward in the forecasting game. We are also finding that we don’t only need to rely on traditional news outlets anymore— as social media and mobile devices are now able to get information out at record speeds.
Now with machine learning algorithms and high-resolution models, we can see tornadoes coming way faster than ever before. And with that kind of lead time people have enough time to react or evacuate safely when necessary.
And if you’re thinking “well how does that help me right now?” Let me tell you! The ability for these portable ground-based observation systems to study these events up close is something that’s never been an option before. This alone provides us insight into the structure and behavior of these things which allows us more knowledge but also gives communities more time when one might be headed their way.
Wrapping Up the Whirlwind: Insights into Tornado Speeds and Safety
Tornadoes are frightening. They’re fast, powerful, and unpredictable. But as I’ve spent more time exploring these fascinating natural disasters with organizations like NASA and NOAA, I’ve also gained a wealth of insights about how they work.
The columns of swirling air that make up these storms, often referred to as a vortex, are both powerful and intriguing to me from a scientific standpoint. They occur worldwide, but North America—particularly its southern plains and the notorious Tornado Alley that stretches from South Dakota to Texas—is most associated with them. In other parts of the world, such as Argentina and Bangladesh, where they also occur in high densities outside the U.S., tornadoes present similar stories of nature’s mighty power.
Thunderstorms have always been electrifying to me (pun intended), especially when their electricity is more literal than figurative like those seen in tornadoes.
During springtime in particular, my mind wanders back to all those hours spent staring at clouds and trying to understand tornado formation by analyzing estimated wind speeds through different altitudes.
While we often think about how terrifyingly loud an average tornado is—its roar often compared to a freight train or low-flying plane—we can’t forget that warnings are designed specifically for saving lives rather than simply predicting where the storm will touch down.
For example, data on destructive tornadoes helped us develop safe rooms capable of withstanding direct hits which protect those hunkering inside from flying debris. That technology could be useful just about anywhere in the world because it is often not used there enough: Outside the U.S., the places with highest concentrations of twisters happen in Argentina and Bangladesh.
When you look back on destruction caused by these kinds of storms, one thing becomes abundantly clear: no amount of safety measures can be considered overkill when they can save lives.
We come closer every day to being able to predict tornados, and the science has improved in leaps and bounds over time. But when it comes down to it, you need to know how to stay safe—and that starts with understanding the basics like the difference between a tornado watch and a warning.
The knowledge we now have about predicting these storms, thanks in part to the National Weather Service, is powerful, but I understand that sometimes staying safe is as simple as being aware of your surroundings. I hope that my findings on tornado speeds and safety serve as an adequate guide for you, so that you can navigate nature’s fury respectfully and cautiously.

